What is Periodontology?
Periodontology deals with the treatment and prevention of gum diseases, which can lead to tooth loss if not treated. These diseases develop when bacteria in the mouth cause infections that affect the gums and structures that hold the teeth to the jawbone. Periodontists are dentists specialized in treating these diseases and maintaining oral health in this area.
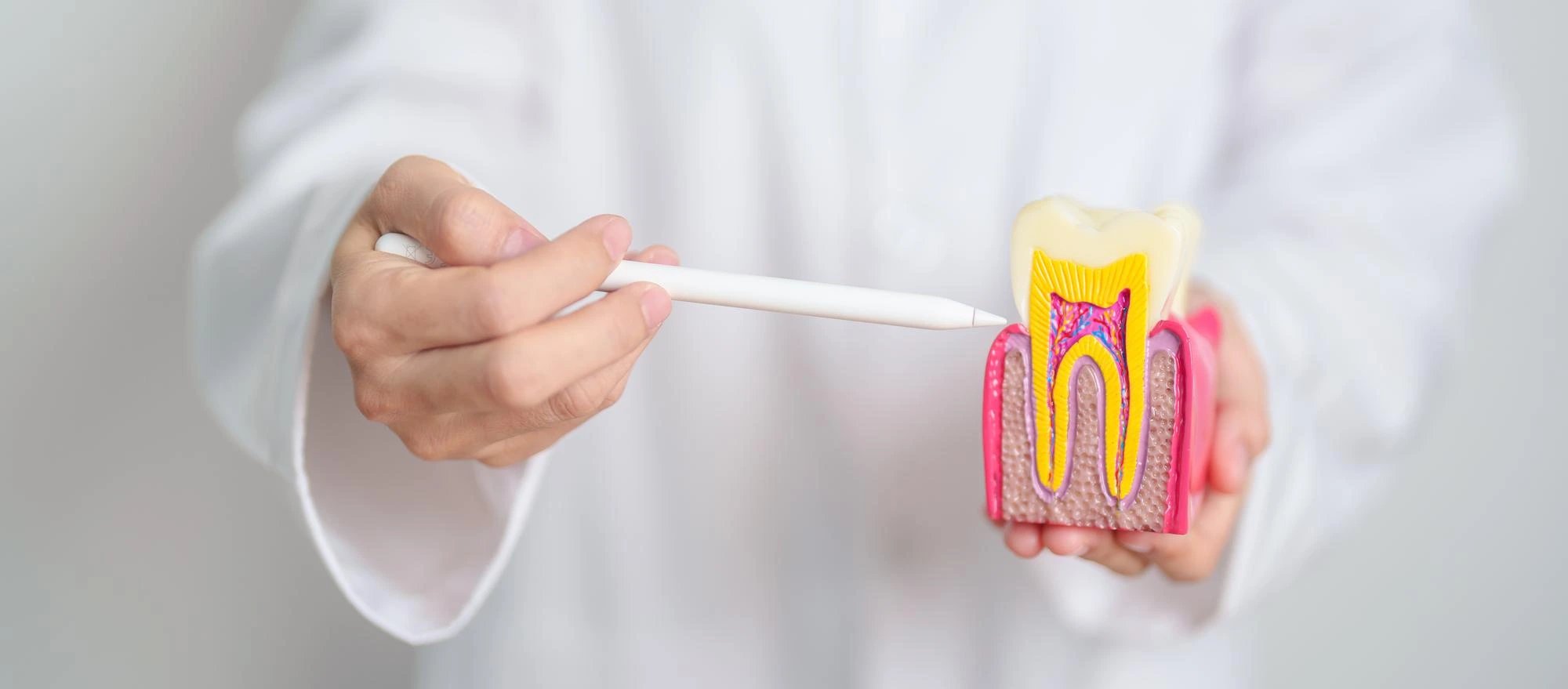
Structure of the Periodontium
The periodontium includes several important elements for the support and function of the teeth, such as:
- Gum tissue (gingiva): The outer part of the periodontium that covers and protects the teeth and surrounding bones. The gums are sensitive and can become inflamed during the development of periodontal diseases.
- Periodontal ligament: A structure that connects the tooth to the jawbone, allowing slight movement during chewing activities.
- Alveolar bone: The bone that supports and holds the teeth in place. This is one of the most important elements that helps keep the teeth in the mouth.
Types of Periodontal Diseases
- Gingivitis is the mildest form of periodontal disease and is usually caused by the accumulation of dental plaque on the gums. This leads to inflammation, redness, and bleeding of the gums, typically during brushing.
- Symptoms: Red and swollen gums, bleeding during tooth brushing, bad breath.
- Gingivitis is reversible and can be treated with careful teeth cleaning and improved oral hygiene.
- Periodontitis is a more severe form of periodontal disease that develops when gingivitis is left untreated and progresses deeper into the structures supporting the teeth. This causes loss of bone and periodontal ligaments, and if not treated, can lead to tooth loss.
- Symptoms: The development of pockets between the teeth and gums, persistent bad breath, receding gums, and possible pain or sensitivity in the teeth.
- Periodontitis often requires more advanced treatments, including deep cleaning (such as scaling and root planing), and in some cases, surgery may be necessary.
This is a rare and more aggressive form of periodontitis that often occurs in young individuals or those who are otherwise healthy in other aspects of their health. It can cause rapid bone and tooth loss.
This is a more common and slower form of periodontitis. Treatment can help control the progression of the disease, but it may have long-term effects on the structure of the teeth and gums.
An abscess is a collection of pus that occurs due to infection in a periodontal pocket and often requires urgent treatment to prevent the spread of the infection.
