What is Implantology?
Benefits of Dental Implants:
- Aesthetic appearance: Implants are much more natural-looking than dentures and can be perfectly customized to restore the appearance of natural teeth.
- Full function: The use of implants can restore the full chewing function and help maintain the shape and function of the jaw.
- Comfort: They are durable and provide a long-term treatment option.
- Preservation of jawbone: After tooth loss, the jawbone may begin to lose mass and volume, while the implant helps prevent this process.
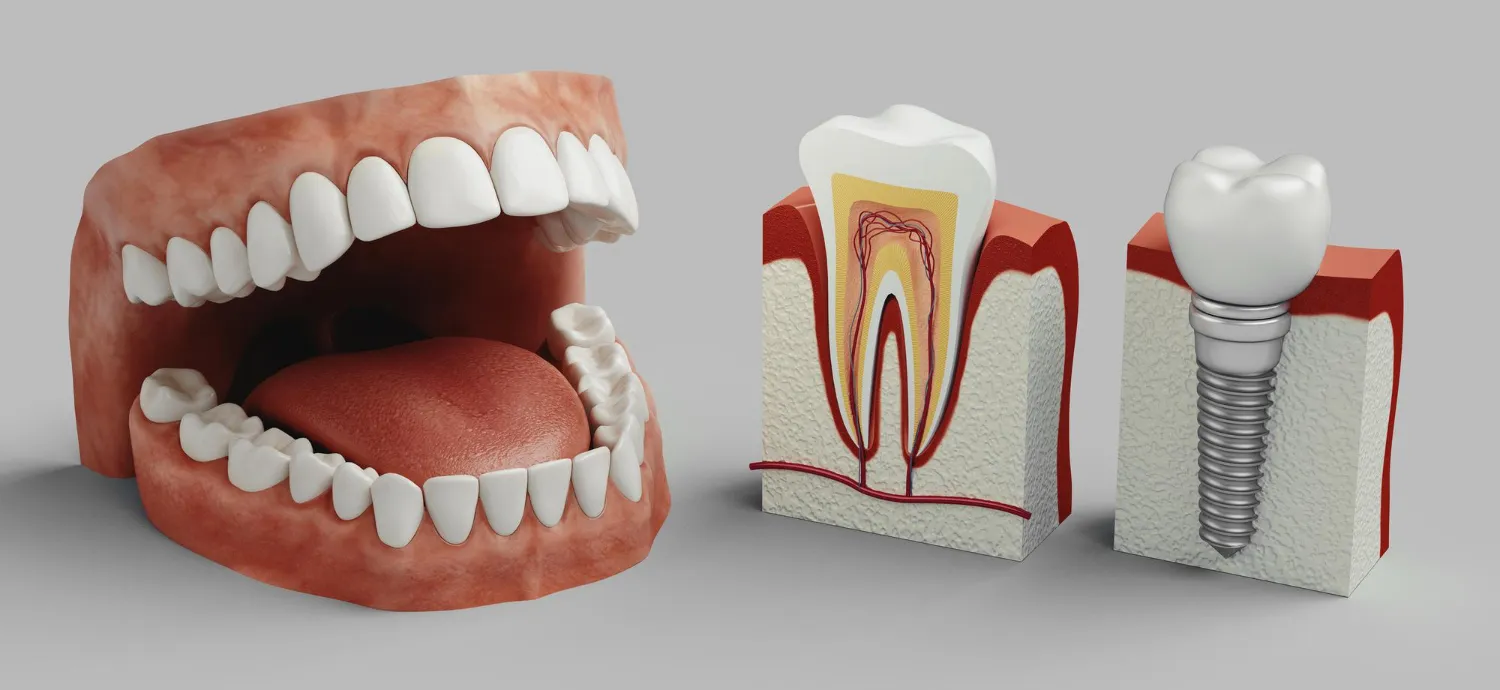
The procedure for placing dental implants:
Assessment and planning: Before any procedure, the dentist will conduct a thorough evaluation of the oral and jaw condition to determine the most suitable plan. Imaging such as X-rays or CT scans may be required to assess internal structures.
Placing the implants: The implant surgeon will perform a surgical procedure to place the implant into the jawbone. This is a safe process and is typically done under local anesthesia. After placement, the implant needs to heal and integrate with the bone over a period of several months, a process called “osseointegration.”
Placement of restorations: After the healing period, the restoration (new tooth, filling, or prosthesis) can be placed over the implants, providing the patient with a functional and aesthetic tooth.
Types of Dental Implants:
The most common and widely used implants are endosteal implants, which are placed directly into the jawbone. They are designed to mimic the shape of a tooth root and are typically made from titanium or titanium alloy.
- Benefits:
- They are highly durable and successful for most patients.
- It provides support for a single tooth, a bridge, or a full denture.
- They integrate well with the jawbone for long-term stability.
- Indications:
- They are used for patients who have sufficient jawbone to support the implants.
Subperiosteal implants are placed beneath the gum tissue but above the jawbone. This type of implant is used when there is insufficient jawbone to support a traditional endosteal implant or when the patient has significant bone loss.
Benefits:
- It can be an option for those who do not have enough bone for an endosteal implant.
- They can be used to support full or partial dentures.
Indications:
- Patients with weak or lost bone, where bone grafting is not a suitable option.
Zygomatic implants are an option for patients with severe bone loss in the upper jaw. They are longer than traditional implants and are placed in the zygomatic bone (the cheekbone area), anchoring into a stronger part of the bone.
Benefits:
- They are suitable for patients who do not have enough bone in the upper jaw to support traditional implants.
- An excellent solution for those who have undergone previous jaw surgeries or significant bone loss.
Indications:
- They are used when there is significant bone loss in the upper jaw, and bone grafting is not a viable option.
This is a technique that uses 4 or 6 implants to support a full prosthesis. This technique is very effective for patients who have lost all their teeth in one jaw and require a permanent solution.
Benefits:
- Very fast, as the patient can have a full fixed prosthesis on the same day as the surgery.
- It is very well-suited for those who have complete tooth loss and want a permanent solution.
Indications:
- Patients who seek a quick and durable restoration for the loss of all teeth in one jaw.
Mini implants are smaller than traditional implants and are typically used for supporting dentures or as an option for patients with weak bone or insufficient space for larger implants.
Benefits:
- Less invasive and can be placed more quickly.
- Ideal for patients who have bone loss and need support for dentures.
Indications:
- They are often used for supporting removable dentures.
Immediate Load Implants are an option that can be placed and immediately loaded with a prosthesis (such as a new tooth or denture) after the surgical procedure.
- Benefits:
- It can improve the aesthetics and function of the patient within the first few days after surgery.
- Ideal for patients who want to avoid long waiting periods to receive their new tooth.
- Indications:
- They are used in specific cases where the bone is strong enough to support the load immediately.
In some cases, implants may fail after placement due to issues such as infections, failure of bone integration, or other complications. In these cases, a second implant may be used to replace the failed one.
